2D Aristotelian diagrams
This page provides a number of 2D Aristotelian diagrams that can be constructed with bitstrings of length 4 (the bitstring representation format is introduced here; more details can be found in Paper P7 and Paper P10). Based on the types of bitstrings they contain, we distinguish various families of:
- Aristotelian squares (or squares of oppositions),
- Aristotelian hexagons (or hexagons of oppositions),
- Aristotelian octagons (or octagons of oppositions).

Aristotelian squares
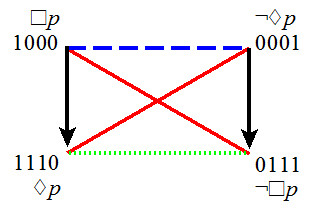
- classical square
- 2 bitstrings of level 1
- 2 bitstrings of level 3
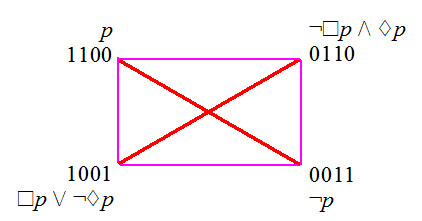
- degenerated square
- 4 bitstrings of level 2
Aristotelian hexagons
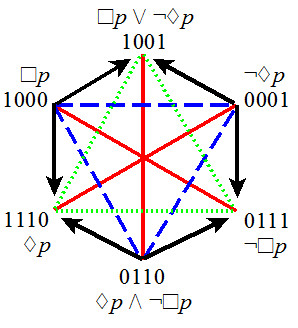
- Jacoby-Sesmat-Blanché hexagon (strong)
- 2 bitstrings of level 1
- 2 bitstrings of level 2
- 2 bitstrings of level 3
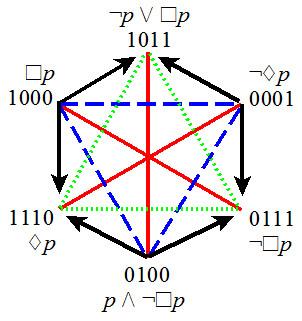
- Jacoby-Sesmat-Blanché hexagon (weak)
- 3 bitstrings of level 1
- 3 bitstrings of level 3
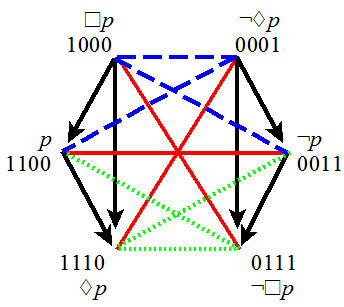
- Sherwood-Czezowski hexagon
- 2 bitstrings of level 1
- 2 bitstrings of level 2
- 2 bitstrings of level 3
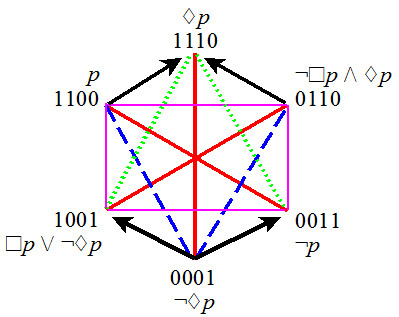
- Unconnected-4 hexagon
(Smessaert-Demey) - 1 bitstring of level 1
- 4 bitstrings of level 2
- 1 bitstring of level 3
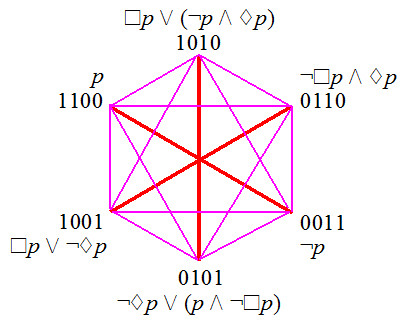
- Unconnected-12 hexagon
(Smessaert-Demey) - 6 bitstrings of level 2
Aristotelian octagons
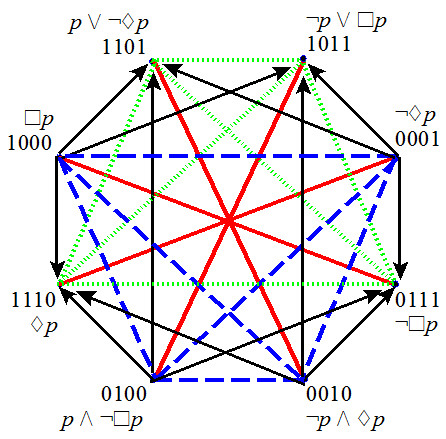
- Moretti-Pellissier octagon
- 4 bitstrings of level 1
- 4 bitstrings of level 2
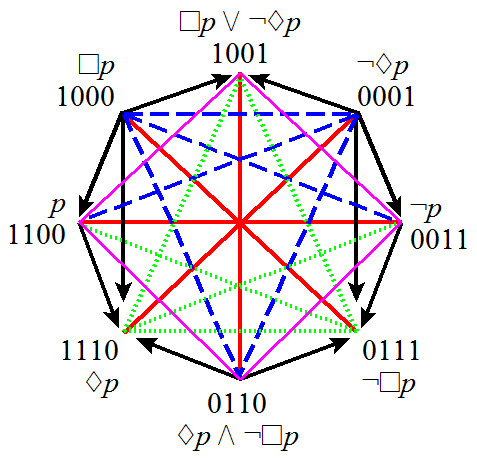
- Béziau octagon
- 2 bitstrings of level 1
- 4 bitstrings of level 2
- 2 bitstrings of level 3
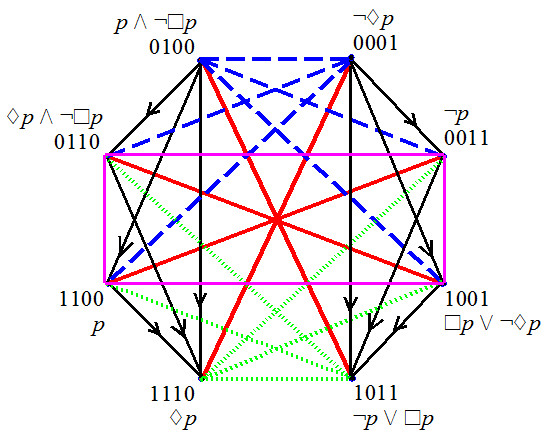
- Buridan octagon
- 2 bitstrings of level 1
- 4 bitstrings of level 2
- 2 bitstrings of level 3